RECORDER Manual
| |
|
|
The bat call filter functionality can help optimizing false triggering on undesired environmental noise signals in passive bat monitoring applications.
The filter mechanism is primarily based on a whistle tracking algorithm that tries to identify more or less pure-tone signals based on their spectral continuity (the amount and direction of frequency modulation) that last for at least a certain minimum duration. This kind of trigger mechanism will work best for relatively long calls with little frequency modulation (low sweep rate, CF calls emitted by bats flying in open spaces). In order to cover also shorter and more intensively frequency-modulated calls (high sweep rate, FM calls emitted by bats flying in cluttered habitats), the software allows to define two different sets of limits (FM and CF) for the sweep rates and minimum durations: one for short FM calls and another for longer CF calls.
See also the principle of the whistle tracking mechanism.
Additional criterions such as the frequency range, high/low frequency magnitude ratio and the magnitude threshold can further limit the trigger events in order to exclude undesired sound events from triggering.
On the Configuration dialog box, the bat call filter option is available on the Trigger type “level of this channel” and can be configured from the bat call filter section on the right-hand side of the Trigger Event section. Alternatively, the Bat Call Trigger Filter Settings dialog box can be launched from the menu Options > Bat call filter trigger settings… (shortcut Ctrl+B).
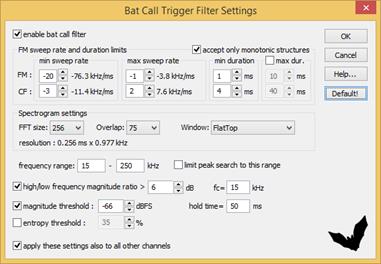
The Bat Call Trigger Filter Settings dialog box includes the following elements:
enable bat call filter : This option activates the bat call filter mode.
accept only monotonic structures : If activated, only monotonic peak frequency shapes will activate the trigger, which will improve the efficiency of the algorithm in detecting whistle-like calls.
FM sweep rate and duration limits : This section defines the limits for the maximum frequency modulation from one time bin to the next and the minimum durations for both the FM and CF call types. The sweep rates are expressed in frequency bins of the spectrogram. The resulting sweep rate (kHz/ms) depends on the sampling rate, the FFT size and the Overlap settings and is displayed on the right of each frequency bin edit box.
min sweep rate : This is the minimum sweep rate limit. Negative values represent falling frequency slopes.
max sweep rate : This is the maximum sweep rate limit. Negative values represent falling frequency slopes.
min duration : This is the minimum duration of the sweep, expressed in milliseconds. Note that the final internal resolution of this setting is limited by the temporal resolution of the real-time spectrogram.
max dur. : If activated, the potential bat calls will additionally compared with the specified maximum durations. If a signal exceeds the defined maximum duration limit, the signal will be rejected. Use this option to for excluding unwanted signals that look similar to bat calls but have a longer duration
Spectrogram settings : The real-time spectrogram settings heavily influence the above sweep rates and their resolution. FFT size: This setting is identical to the corresponding parameter on the Configuration dialog box. Overlap: This setting is identical to the corresponding parameter on the Configuration dialog box. The resulting time and frequency resolution of the spectrogram is indicated ms x kHz.
frequency range : This setting is identical to the corresponding parameter on the Configuration dialog box and determines the frequency interval that is processed.
limit peak search to this range : If activated, the peak search of the tracking algorithm will be limited to the selected frequency range. Deactivating this option (= peak search on the full spectrum) will lower the risk to falsely recognize broad-band noise signals such as rain drops or wind noise as valid bat calls.
high/low frequency magnitude ratio : If activated, the program will calculate an additional spectral parameter that can help to reject unwanted noise. It separates the frequency scale of the FFT spectrum at the specified frequency fc into two sections, determines the peak magnitude for both sections and then calculates the ratio between the two. A detected signal will then only be regarded as a valid bat call if the calculated ratio exceeds the specified threshold (expressed in dB).
magnitude threshold : If activated, this option will a additionally reject lowlevel signals. The threshold corresponds to the Level threshold on the Configuration dialog box but is expressed in dBFS. This (red colored) threshold can be adjusted graphically by selecting the Display option “energy in f-range”.
entropy threshold : If activated, this option will a additionally reject noise signals exhibiting a minimum Wiener entropy value above the specified threshold. This (green colored) threshold can be adjusted graphically by selecting the Display option “energy in f-range”.
Hold time : This hold time determines how close calls or calls with a short silent section in them are treated by the detection algorithm: If the silent interval between two consecutive calls is shorter than the defined holdtime, then the two calls will be treated a single call.
apply these settings to all other channels : If activated, this option will copy the settings for the selected channel also to all other channels.
Default : Sets all parameters to their defaults. Alternatively, these defaults can also be set from the command Options > Configuration management > Presets > Bat Monitoring with bat call filter.
Due to the complexity of the settings, it is recommended to start with the Default settings and perhaps disable the options “high/low frequency magnitude ratio” and “magnitude ratio”. The best settings for a specific set of bat call echolocation calls can be found by testing and optimizing the various settings by trying it with .wav files that have been previously recorded. This mode of operation can be activated by selecting the “Device” “WAV file” on the RECORDER Configuration dialog box instead of the physical recording device.
Successfully detected bat calls are indicated by red markers at the top of the real-time spectrogram display.
While it is in most cases relatively easy to safely detect relatively long CF or QCF calls, it can be a challenge to distinguish very short FM calls by Myotis bat species (which are by the way not intended for long-distance echolocation by animals themselves) from other broad-band noise signals. It might therefore be that the detection of these short FM calls does not work very well. Under these circumstances it is recommended to use the normal threshold-based trigger mechanism instead (bat call filter and whistle tracking options disabled).
|
|