SASLab Manual
| |
Main window : File > Specials > Frequency Division Bat Detector Emulation >
|
|
This Frequency Division Bat Detector Emulation menu allows to convert a high-speed sampled bat sound file into a low-frequency sound file that corresponds to the output signal of a common frequency division bat detector. This feature might be helpful for comparing time-expanded bat sound recordings with frequency division bat sound recordings.
The Settings... drop-down menu command allows to set-up a few parameters for the bat detector emulation.
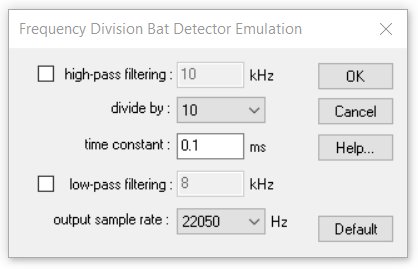
There are several options that influence the conversion results:
high-pass filtering
Checking this option will apply an additional high-pass filter prior to the frequency division procedure. If there is any noise below the bat calls or if there is a constant offset voltage, it is recommended to enable this option.
divide by
This is the frequency division ratio. Most common bat detectors use a division ratio of 10.
time constant
The time constant determines the behavior of the internal envelope tracking. A value of about 0.1 milliseconds would be appropriate.
low-pass filtering
Checking this option will apply an additional low-pass filter to the output signal of the frequency division procedure. This might help reducing unwanted (spurious) harmonics that are inherent to the frequency division technique.
output sample rate
This is the final sample rate of the resulting sound file. 22050 Hz should be appropriate for common applications. However, in some cases it might be useful to increase the sample rate in order to cover higher frequencies.
The Default button sets all parameters to their defaults.
The command Convert file executes the file conversion according to the settings made on the Frequency Division Bat Detector Emulation Settings dialog box. The original sound file must have the original (or natural) time axis scaling. If the recording has been made using a time-expansion bat detector, the sample rate entry in the file header must be multiplied by the expansion ratio (e.g. 22050 Hz * 10 = 220500 Hz).
|
|